1. Matter :- Things that have mass and value and occupy space.
2. Panch Tatva:- Early Indian philosophers classified matter in the form of five basic elements..........air, earth, fire, sky and water.
They said all living and non-living things are made up of these basic elements.
3. Basis of classification of matters:-
(a) Physical Property of matter
(b) Chemical Property
4. Matter is made up of small particles.
5. Characteristics of particles of matter :-
(A) They have space between them . This space is called interparticle space.
(B) They continuously move.
(C) They attract each other.
6. Particles of matter have kinetic energy that is why they are continuously moving.
7. With increase in temperature , the kinetic energy of the particles also increases.
8. On heating diffusion becomes faster.
9. The intermixing of particles of two different types of matter on their own by getting into the interparticle spaces is called diffusion.
10.The strength of force of attraction between the particles of matter varies from one kind of matter to another.
11. There are three states of matter:-
a. Solid
b. Liquid
c. Gas
12. Gas and Liquid are grouped under "Fluid".
13. Technically speaking a fourth state of matter called plasma exists, but it does not naturally occur on earth.
And 5th state of matter is known as Bose-Einstein Condensate.
14. SOLID:-
A solid has fixed shape.
Some solid change their shape under force but regain its shape when the applied force is removed.
A solid has fixed volume.
A solid is hardly compressible on applying pressure.
Particles of solid have negligible kinetic energy.
A solid doesn't have the property of diffusion.
15. LIQUID:-
A liquid has no fixed shape.
It has fixed volume.
It takes the shape of the container in which it is kept.
It has fluidity.
It has lesser density as compared to solid.
Its particles have more kinetic energy that that of solid.
Particles in liquid state easily diffuse.
16. GAS:-
It has the lowest density and fill its containers completely.
It has no fixed shape.
It has maximum fluidity and least rigidity.
It doesn't keep its volume and are highly compressible.
It is generally light.
Its kinetic energy is very high.
It exerts pressure.
It diffuses easily.
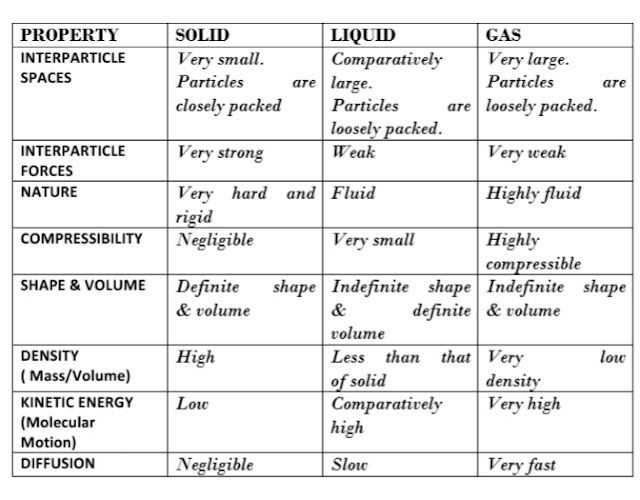
17. COMPARISON CHART OF THREE STATES OF MATTER
18. Change of state of matter:- (Effect of temperature)
(A) When temperature of solids is increased , the kinetic energy of the particles increases. Thus the particles start vibrating with great speed. When the energy supplied by the heat overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles, the particles leave their fixed position and start moving freely.Finally solids get converted into liquids.
(B) When heat energy is supplied to water, particle start moving faster.At a certain temperature, the particles of water have enough energy to break free the forces of attraction of each other.Thus water starts changing into vapour.
19. Melting point:-
■Melting point of a solid indicates the strength of the force of attraction between its particles.
■Melting point is the temperature at which a solid melts to liquid at the atmospheric pressure.
20.Fusion:- Change of a matter from its solid state into liquid state is called fusion.
21.Latent heat of fusion:- The amount of heat energy required to change 1Kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the latent heat of fusion.
22. Vaporization :-
▪︎Heat absorbed when a liquid vaporizes.
▪︎Vaporization is the conversion of a substance from the liquid or solid phase into the gaseous (vapour) phase.
▪︎The phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapours at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
23.Latent heat of vaporisation:- The quantity of heat required at a specified temperature to convert unit mass of liquid into vapour.
Or
The amount of heat energy required to convert 1kg of a liquid at its boiling point temperature into its vapour state without any rise in temperature.
24.Boiling:- When heat is supplied and there is formation of vapour bubbles within a liquid, the vaporization process is called boiling.
■Boiling is a bulk phenomenon. Particles from the bulk(whole) of the liquid change into vapour state.
25.Boiling Point:- The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is called its boiling point.
26. Sublimation:- A change of state of matter from solid to gas without changing into liquid state or vice versa is called sublimation.
Naphthalene balls, camphor, iodine, ammonium chloride etc. undergo sublimation.
27. Change of state of matter:-
(Effect of pressure)
Applying pressure and reducing temperature liquefy gases.
28. Dry Ice ( Solid Carbon dioxide) :-
•It is Carbon dioxide stored under high pressure.
•It gets converted directly into gaseous state on decrease of pressure to 1 atm without undergoing liquid state.
29.Interconversion of the three states of matter:


30. Latent Heat:- Latent heat is the energy absorbed or released by a substance during a change in its physical state without changing its temperature.
*Or*
Latent Heat – The heat energy which is used to break the force of attraction between the particles of matter is known as latent heat. Since the heat is hidden therefore it is called as Latent Heat.
▪︎Latent heat is absorbed upon evaporation.
▪︎Latent heat is released upon condensation to liquids as in clouds.
31.Atmospheric Pressure (barometric pressure) :- Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted against a surface by the weight of the air above that surface.
Or
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by gas particles in Earth’s atmosphere as those particles collide with objects.
▪︎Atmospheric pressure decreases as altitude increases.
▪︎The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as 101,325 Pa.
32.Freezing :- It is the process that causes a substance to change from a liquid to a solid. is the process that causes a substance to change from a liquid to a solid.
33. Freezing Point:- The freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid changes to a solid by giving out heat energy. The freezing point of a substance is not necessarily the same as its melting point.
Questions
1. Is rubber band solid?
It is solid.It changes its shape under force & regains its shape when the force is removed.
2. Why are liquids and gases fluids?
Liquids & gases flow and change their shape so they are not rigid. They are fluids.
3. How is diffusion of gas in water useful ?
The gases from the atmosphere diffuse and dissolve in water. These gases especially Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide are essential for aquatic organisms also. These aquatic organisms breathe under water due to presence of Oxygen in water.
4. Gases completely fill any container in which they are placed.Why?
It is because intermolecular forces of gases are relatively weak, so their molecules are constantly moving independently of the other molecules present.
5. Why solids are dense, rigid, and incompressible?
It is because their intermolecular forces are so strong that the molecules are essentially locked in place.
6. How the compressibility of gas is useful?
Due to high compressibility large volume of gas can be compressed into a small cylinder and transported easily.LPG and CNG are compressed gases.
7. How does smell ( for example smell coming out of kitchen) reach us even farther away?
Or
The smell of hot cooked food reach us in seconds, why?
As the food is hot, so the aroma of food shows the property of diffusing very fast into the particles of air ( that have large space between them also) spread from the kitchen and reach us fast.
8. A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.Why?
Particles in a gas have high kinetic energy, they move at a brisk speed & strike the walls of the container with force. Thus they exert pressure on the walls of the container.
9. When a solid melts, its temperature remains the same, so where does the heat energy go?
As long as the solid does not melt, the temperature will rise. Once the melting starts, the temperature becomes constant till the whole solid melts as heat energy is now consumed in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles.
As the heat energy is absorbed by the solid without showing any rise in temperature, it is considered that it gets hidden into the content and this heat is said to be the latent heat of fusion.
10. Water vapour at 373 K ( 100°C) have more energy than the water at the same temperature. Why?
This is because particles in steam have absorbed extra energy in the form of latent heat of vaporisation.
11. What will happen when we start putting pressure and compress a gas enclosed in a cylinder?
If we start putting pressure on a gas enclosed in a cylinder then the gas will be compressed and become liquid.
Eg.- CNG and LPG are formed by compressing it in a similar way that increasing the pressure and decreasing the temperature changes their state from gas to liquid.
NCERT EXEMPLAR QUESTION
Multiple Choice Questions
1.Which one of the following sets of phenomena would increase on raising the temperature?
(a) Diffusion, evaporation, compression of gases
(b) Evaporation, compression of gases, solubility
(c) Evaporation, diffusion, expansion of gases
(d) Evaporation, solubility, diffusion, compression of gases
Answer & Explanation:-(c)If temperature increases; rate of evaporation, diffusion and expansion of gases increase.
2. Seema visited a Natural Gas Compressing Unit and found that the gas can be liquefied under specific conditions of temperature and pressure. While sharing her experience with friends she got confused. Help her to identify the correct set of conditions.
(a) Low temperature, low pressure
(b) High temperature, low pressure
(c) Low temperature, high pressure
(d) High temperature, high pressure
Answer & Explanation:- (c) When gases is compressed under low temperature and high pressure, the gas lequifies.
3. The property to flow is unique to fluids. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Only gases behave like fluids.
(b) Gases and solids behave like fluids.
(c) Gases and liquids behave like fluids.
(d) Only liquids are fluids.
Answer & Explanation:- (c) Gases and liquids flow due to less intermolecular force in the molecules. Gases and liquids take the shape of the container in which they are kept.
4. During summer, water kept in an earthen pot becomes cool because of the phenomenon of
(a) diffusion
(b) transpiration
(c) osmosis
(d) evaporation.
Answer & Explanation:- (d) Earthen pot has small pores through which water keeps evaporating which causes cooling.
5. A few substances are arranged in the increasing order of ‘forces of attraction’ between their particles. Which one of the following represents a correct arrangement?
(a) Water, air, wind
(b) Air, sugar, oil
(c) Oxygen, water, sugar
(d) Salt, juice, air
Answer & Explanation:-(c) Forces of attraction between the particles increase in the order of gases < liquids < solids hence, the correct arrangement is oxygen, water, sugar.
6. On converting 25°C, 38°C and 66°C to Kelvin scale, the correct sequence of temperature will be
(a) 298 K, 311 K and 339 K
(b) 298 K, 300 K and 338 K
(c) 273 K, 278 K and 543 K
(d) 298 K, 310 K and 338 K
Answer & Explanation:- (a) K =25 °C + 273
Hence 25°C = 273 + 25 = 298 K
38°C = 273 + 38 = 311 K
66°C = 273 + 66 = 339 K
7. Choose the correct statement of the following.
(a) Conversion of solid into vapours without passing through the liquid state is called vapourisation.
(b) Conversion of vapours into solid without passing through the liquid state is called sublimation.
(c) Conversion of vapours into solid without passing through the liquid state is called freezing.
(d) Conversion of solid into liquid is called sublimation. ’
Answer & Explanation:-(b) Conversion of vapours into solid without passing through the liquid state is called sublimation.
8.The boiling points of diethyl ether, acetone and n-butyl alcohol are 35°C, 56°C and 118°C respectively. Which one of the following correctly represents their boiling points in Kelvin scale?
(a) 306 K, 329 K, 391 K
(b) 308 K, 329 K, 392 K
(c) 308 K, 329 K, 391 K
(d) 329 K, 392 K, 308 K
Answer & Explanation:-
(c): 35°C = 273 + 35 = 308 K
56°C = 273 + 56 = 329 K
118°C = 273 + 118 = 391 K
9.Which condition out of the following will increase the evaporation of water?
(a) Increase in temperature of water
(b) Decrease in temperature of water
(c) Less exposed surface area of water
(d) Adding common salt to water
Answer & Explanation:- (a): Rate of evaporation increases with increase in temperature of water.
10. ln which of the following conditions, the distance between the molecules of hydrogen gas would increase?
(i) Increasing pressure on hydrogen contained in a closed container.
(ii) Some hydrogen gas leaking out of the container.
(iii) Increasing the volume of the container of hydrogen gas.
(iv) Adding more hydrogen gas to the container without increasing the volume of the container.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii)and(iv)
Answer & Explanation:- (c) (ii) If some hydrogen gas is leaked from the container the remaining gas will occupy the whole space but the distance between the molecules will increase.
(iii) If the volume of the container is increased, same number of molecules will occupy that space. Hence, the distance between the molecules will increase.
Short Answer Question
11. A sample of water under study was found to boil at 102°C at normal temperature and pressure. Is the water pure? Will this water freeze at 0°C? Comment.
Answer:-The sample of water boils at a higher temperature due to impurities present in it . Due to non-volatile impurity this water will freeze below 0°C.
12.A student heats a beaker containing ice and water. He measures the temperature of the content of the beaker as a function of time. Which of the following (Fig. 1.1) would correctly represent the result? Justify your choice.
Answer: (d) Since ice and water are in equilibrium, the temperature would be zero. When we heat the mixture, ‘energy supplied is utilised in melting the ice and the temperature does not change till the ice melts because of latent heat of fusion. On further heating the temperature of the water would increase. Therefore (d) is the correct option.
13.Fill in the blanks:
(a) Evaporation of a liquid at room temperature leads to a cooling effect.
(b) At room temperature the forces of attraction between the particles of solid substances are stronger than those which exist in the gaseous state.
(c) The arrangement of particles is less ordered in the liquid, gaseous state. However, there is no order in the state.
(d) Sublimation is the change of gaseous state directly to solid state without going through the liquid state.
(e) The phenomenon of change of a liquid into the gaseous state at any temperature below its boiling point is called Evaporation.
14. Match the physical quantities given in column A to their SI units given in column B.
Column (A) Column (B)
(a) Pressure (i) cubic metre
(b) Temperature (ii) kilogram
(c) Density (iii) pascal
(d) Mass (iv) kelvin
(e) Volume (v) kilogram per cubic metre
Solution:
(a) (iii) (b) (iv) (c) (v) (d) (ii) (e) (i)
15.The non SI and SI units of some physical quantities are given in column A and column B respectively. Match the units belonging to the same physical quantity.
Column (A) Column (B)
(a) Degree Celsius (i) kilogram
(b) Centimetre (ii) pascal
(c) Gram per centimetre cube (iii) metre
(d) Bar (iv) kelvin
(e) Milligram (v) Kg per metrecube
Solution: (a) (iv) (b) (iii) (c) (v) (d) (ii) (e) (i)
16. ‘Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion’. Comment.
Answer:- In diffusion, the particles move from higher concentration to lower concentration without separation by a semipermeable membrane. In osmosis, the particles move from lower concentration to higher concentration (solvent to solution) when the two solutions are separated by a semipermeable membrane. Hence, osmosis is a special kind of diffusion.
17.Classify the following into osmosis/diffusion:
(a) Swelling up of a raisin on keeping in water. Osmosis
(b) Spreading of virus on sneezing. Diffusion
(c) Earthworm dying on coming in contact with common salt. Osmosis
(d) Shrinking of grapes kept in thick sugar syrup. Osmosis
(e) Preserving pickles in salt. Osmosis
(f) Spreading of smell of cake being baked throughout the house. Diffusion
(g) Aquatic animals using oxygen dissolved in water during respiration. Diffusion
18. Water as ice has a cooling effect, whereas water as steam may cause severe burns. Explain these observations.
Answer: Water in the form of ice has low energy since water freezes at a lower temperature. When ice comes in contact with body it draws heat from the body and gives cooling effect. In case of steam, the water molecules have high energy. The high energy of steam is transformed as heat and may cause severe burns.
19. Alka was making tea in a kettle. Suddenly she felt intense heat from the puff of steam gushing out of the spout of the kettle. She wondered whether the temperature of the steam was higher than that of the water boiling in the kettle. Comment.
Answer:The temperature of both boiling water and steam is 100°C but steam has more energy because of latent heat of vaporisation. Hence, steam is hotter than boiling water.
20. A glass tumbler containing hot water is kept in the freezer compartment of a refrigerator (temperature < 0°C). If you could measure the temperature of the content of the tumbler, which of the following graphs (Fig. 1.2) would correctly represent the change in its temperature as a function of time.
Answer:-(a) The hot water in the glass tumbler kept in freezer will first become cold and the temperature will drop till 0°C. At 0°C, water loses heat equal to latent heat of fusion till entire water freezes to form ice at 0°C. During this change of state from liquid to solid, the temperature remains constant.
On still further cooling, the temperature of ice slowly falls with time. Therefore, the correct option is (a).
21.Look at Fig. 1.3 and suggest in which of the vessels A, B, C or D the rate of evaporation will be highest? Explain.
Answer:-The rate of evaporation depends on the surface area of the container. More the surface area, more is the evaporation. It also depends on the speed of the wind. If speed of the wind is more, more number of particles will evaporate from the surface. Hence, the figure (C) in which both these factors, surface area and moving fan are there, the rate of evaporation will be maximum.
22. (a) Conversion of solid to vapour is called sublimation. Name the term used to denote the conversion of vapour to solid.
(b) Conversion of solid state to liquid state is called fusion; what is meant by latent heat of fusion?
Answer:
(a) Sublimation
(b) Latent heat of fusion is the amouunt of heat required to change 1 kg solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point.
Long Answer Question:-
23.You are provided with a mixture of naphthalene and ammonium chloride by your teacher. Suggest an activity to separate them with well labelled diagram.
Answer:- Mixture of naphthalene and ammonium chloride can be separated as follows :
Step-1: Put the mixture in a beaker and add water to it. Stir with a glass rod. Ammonium chloride being soluble in water gets dissolved leaving behind the insoluble naphthalene.
Step-2: Filter the solution. Naphthalene remains on the filter paper while ammonium chloride is obtained as filtrate.
Step-3: Evaporate the filtrate to get back ammonium chloride.
OR
24.lt is a hot summer day, Priyanshi and Ali are wearing cotton and nylon clothes respectively. Who do you think would be more comfortable and why?
Answer:- Priyanshi is wearing cotton clothes which are more comfortable in summers because cotton absorbs the sweat which causes cooling on evaporation. Ali is wearing nylon clothes which do not absorb sweat. Hence, Ali will be uncomfortable.
25.You want to wear your favourite shirt to a party, but the problem is that it is still wet after a wash. What steps would you take to dry it faster?
Answer: The process of drying the shirt can be made faster through the following ways :
(a) Spread the shirt to increase the surface area which will increase rate of evaporation.
(b) Put it in the sun to increase the temperature to increase the rate of evaporation.
(c) Keep it under the fan to increase the wind speed which increases the rate of evaporation.
These are the conditions that can increase the rate of evaporation.
26.Comment on the following statements:
(a)Evaporation produces cooling.
(b)Rate of evaporation of an aqueous solution decreases with increase in humidity.
(c)Sponge though compressible is a solid.
Answer:-
(a) Evaporation is a surface phenomenon. The particles from the surface of the liquid take energy from the surroundings and change into vapours which results in the decrease in energy of the surroundings,thereby producig cooling effect .
(b) The amount of water present in the air is known as humidity. If the water vapour in air is already present in large amount, it is not able to take up more water through evaporation. Hence, the rate of evaporation of water will decrease. On a dry day, the air absorbs water more readily hence, the rate of evaporation is high on a dry day.
(c) Sponge is solid but it has minute pores in which air is trapped. These pores make the sponge a soft material. When sponge is pressed, the air present in the pores expels out and the sponge is compressed.
27.Why does the temperature of a substance remain constant during its melting point or boiling point?
Answer:-When a substance melts, it absorbs heat for the conversion of solid state into liquid state. As we continue heating, the heat supplied is used up in converting the solid state into liquid state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles and there is no change in temperature till the whole solid is converted into liquid. This is called latent heat of fusion.
When a liquid is heated, it starts converting into vapours. Further heat given to the liquid is used in changing the state and there is no increase in the temperature till the liquid starts boiling. This heat is known as latent heat of vaporisation. Hence, the temperature of a substance remains constant at its melting point or boiling point untill all the substance melts or boils.
Important Links:-
For answer to the questions given in NCERT BOOK,Copy and paste the following link into Google Search
https://www.tetsuccesskey.com/2015/08/matter-in-our-surroundings-NCERT-Solutions.html
To know more about 4th & 5th state of matter visit chem4kids.com
Some applications of latent heat
http://heatmozac.blogspot.com/2008/09/43-specific-latent-heat-appications.html?m=1








Comments
Post a Comment